Finishing
Finishing is a process to enhance the surface properties of materials. It uses methods like coating, plating, and heat - treatment. Ideal for improving corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetics, it's widely used in automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods industries.
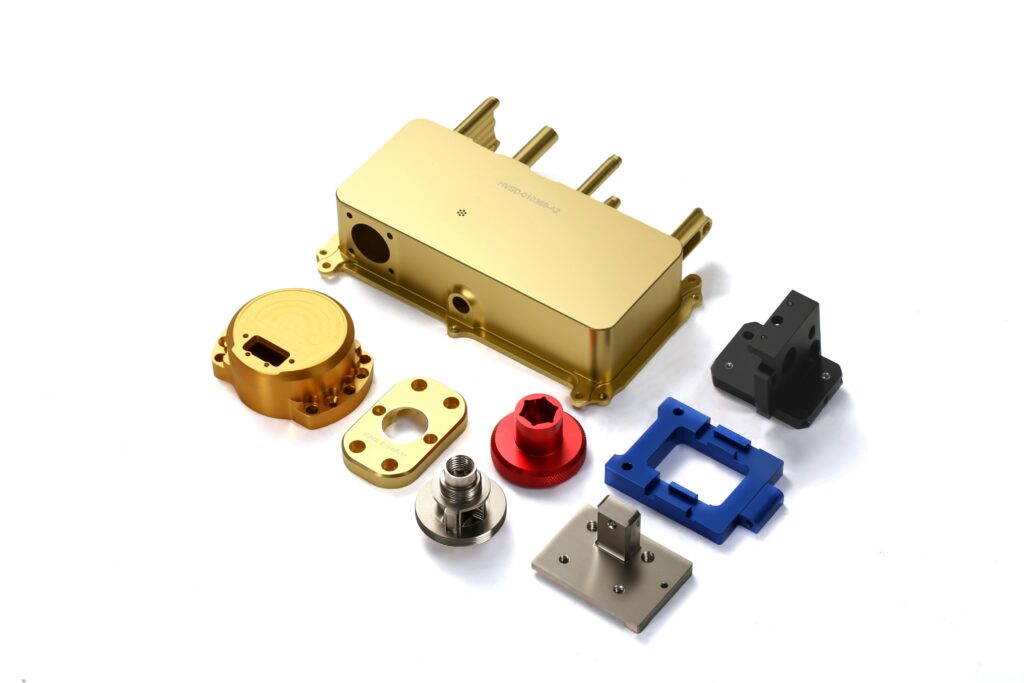

Type
Introduction
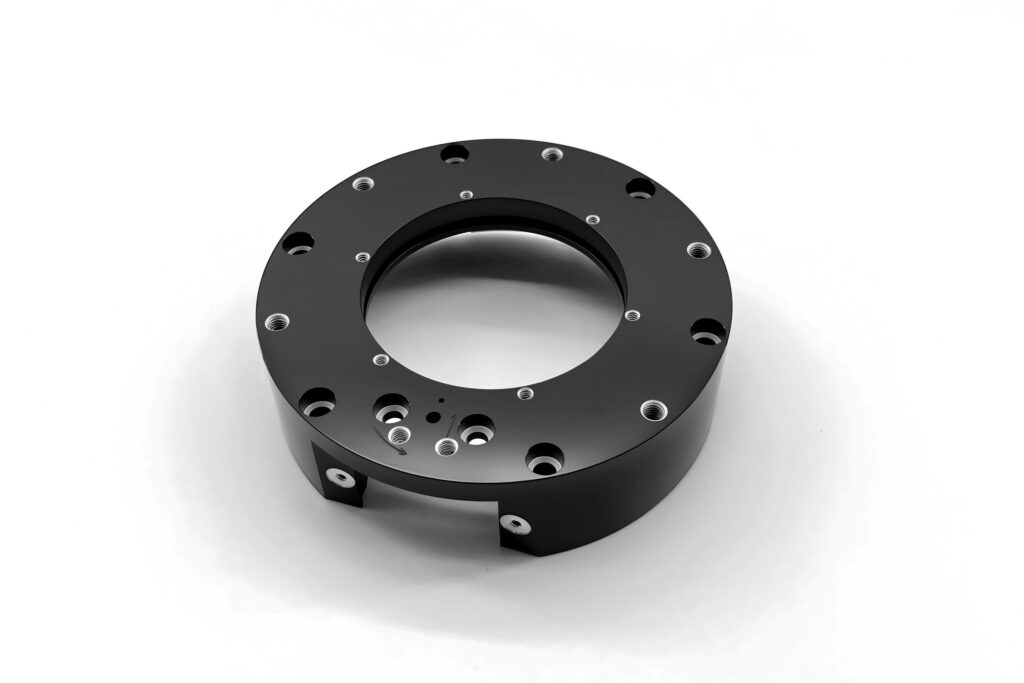
Anodizing
An electrochemical process forming a protective oxide layer on metals (mainly aluminum), boosting corrosion resistance and enabling dyeing. Used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
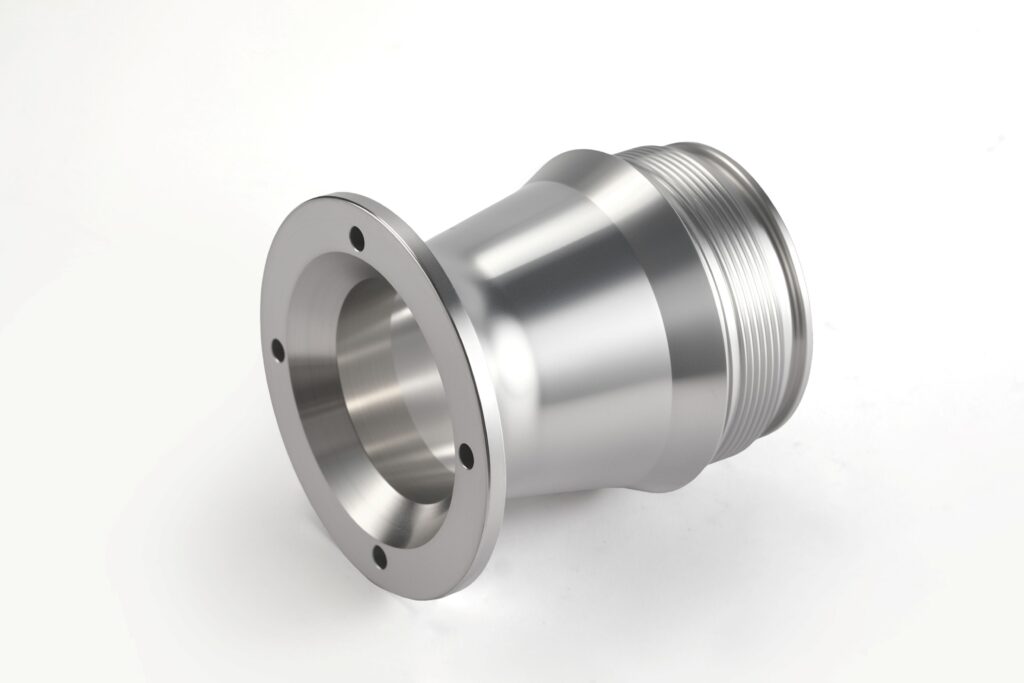
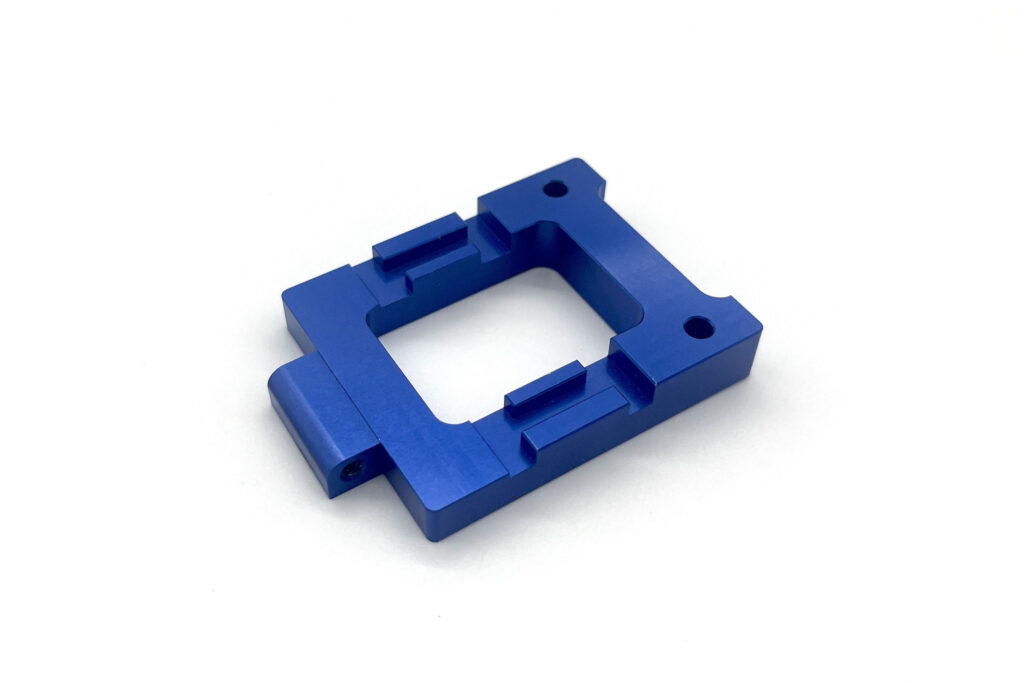
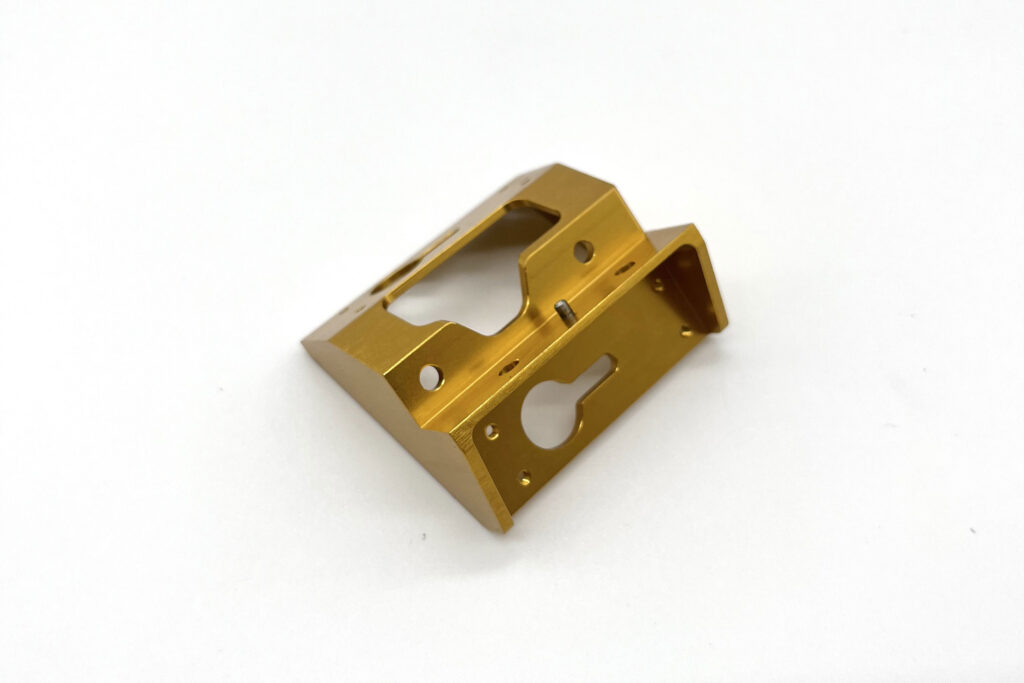
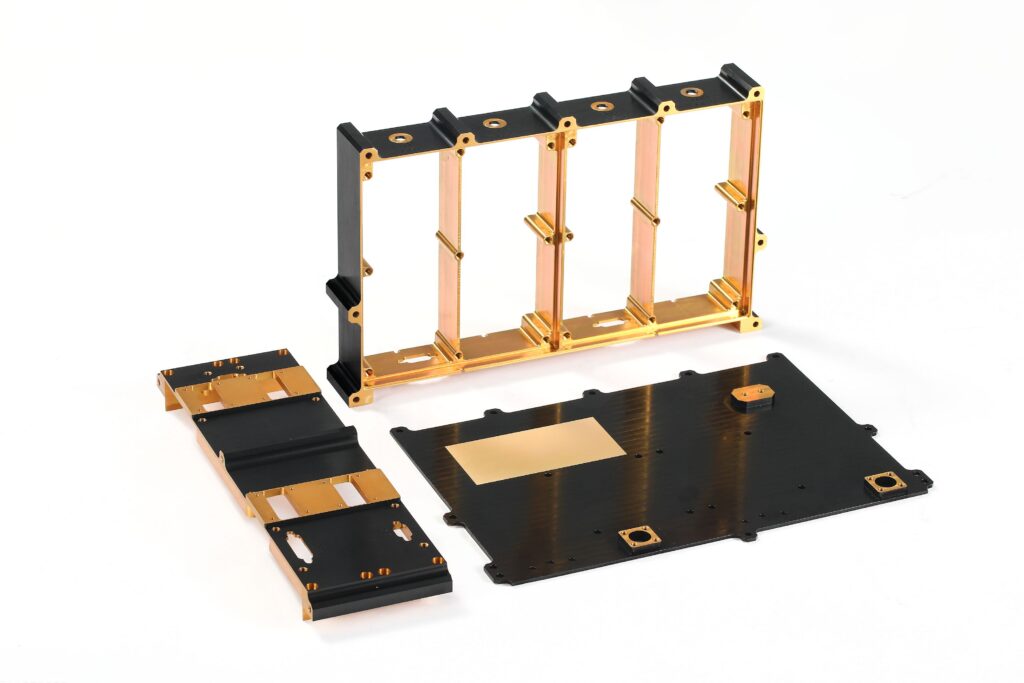




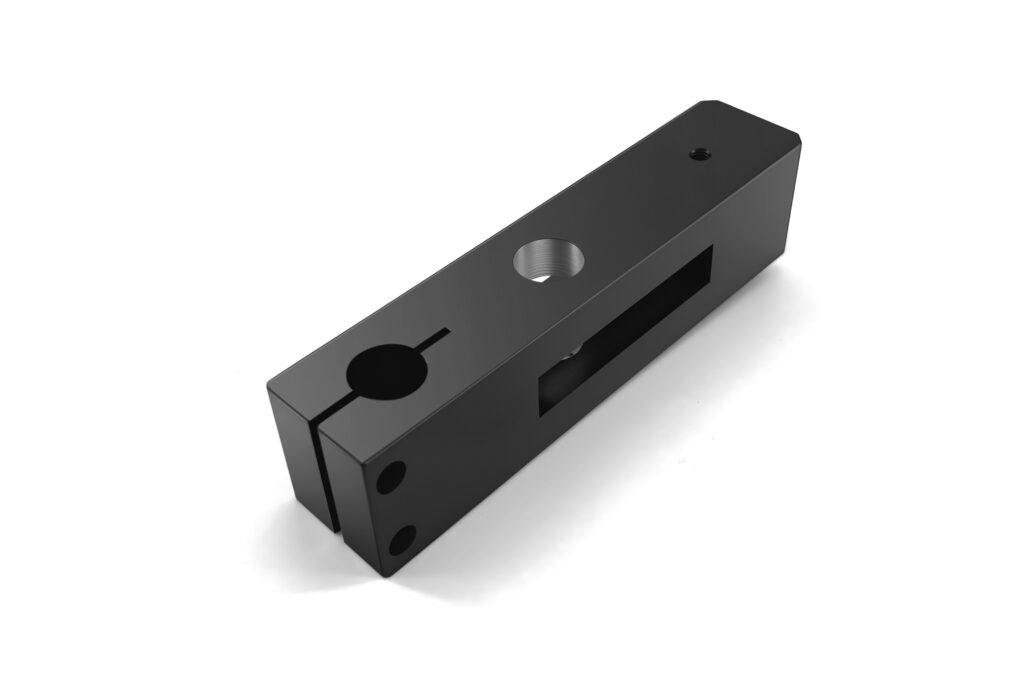
Powder Coating
Dry painting method where electrostatically applied powder adheres to metal surfaces and is then heat-cured into a tough, protective layer. Used in Aerospace, Automotive,Medical,Industrial Equipment,Household Appliances,Building Materials,etc.
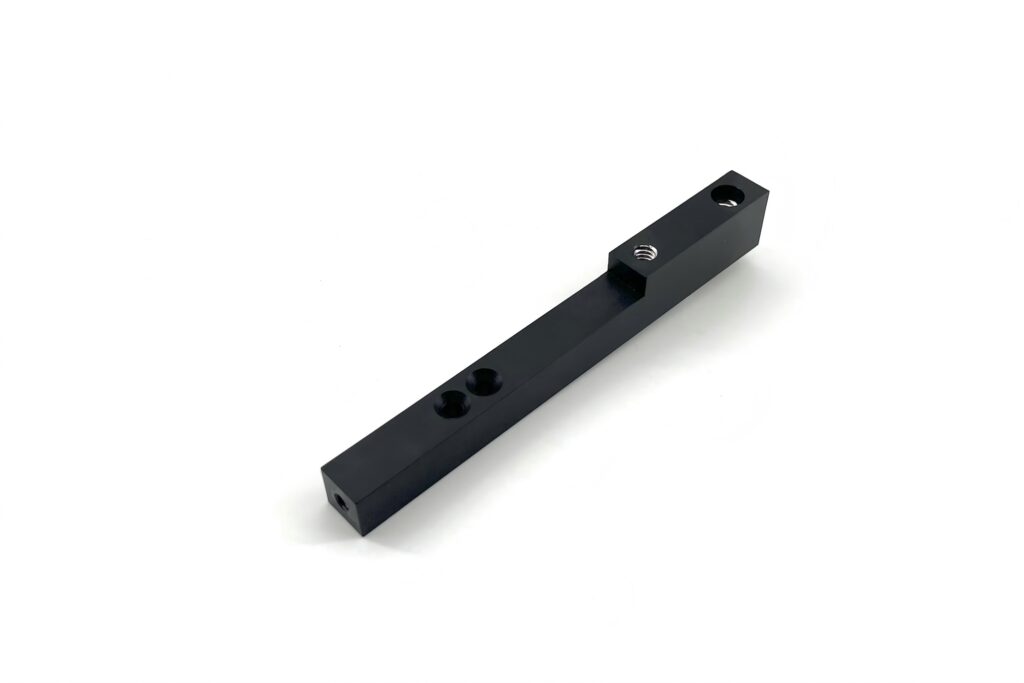
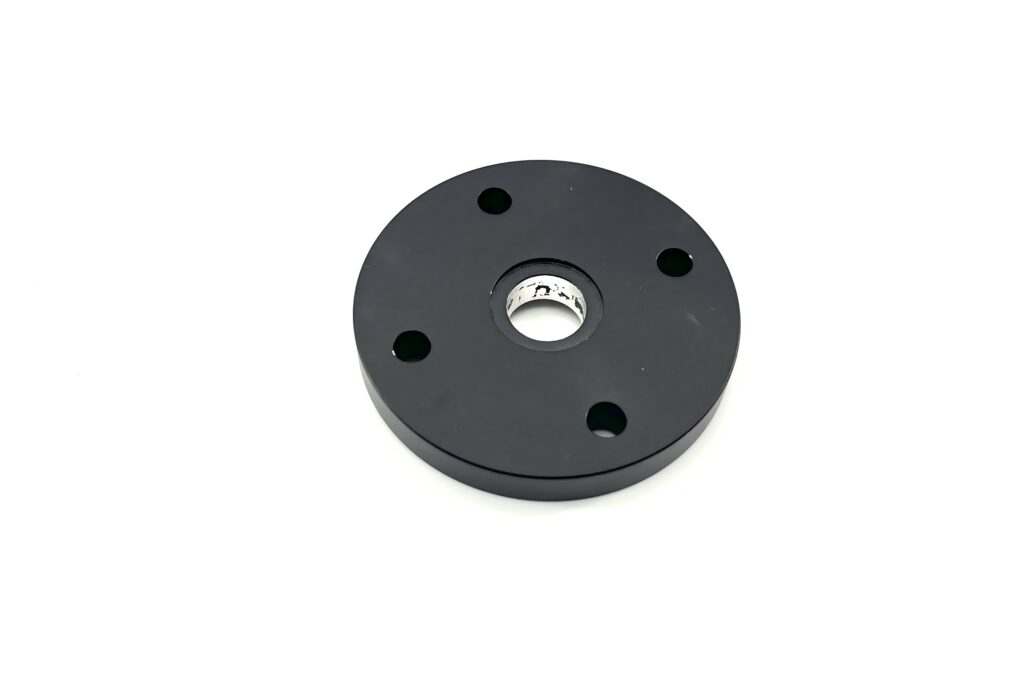
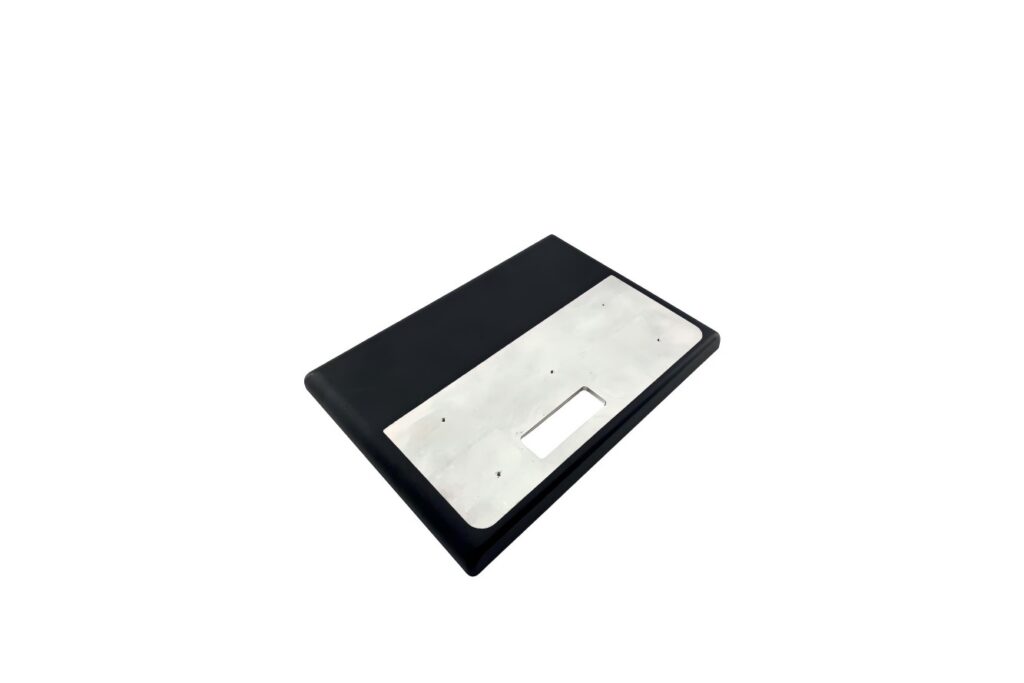



Heat Treatment
Involves heating, holding, and cooling metals or alloys to alter their microstructure, thereby improving properties like hardness, strength, toughness, and wear resistance.Used in Aerospace, Automotive,and Tool manufacturing.
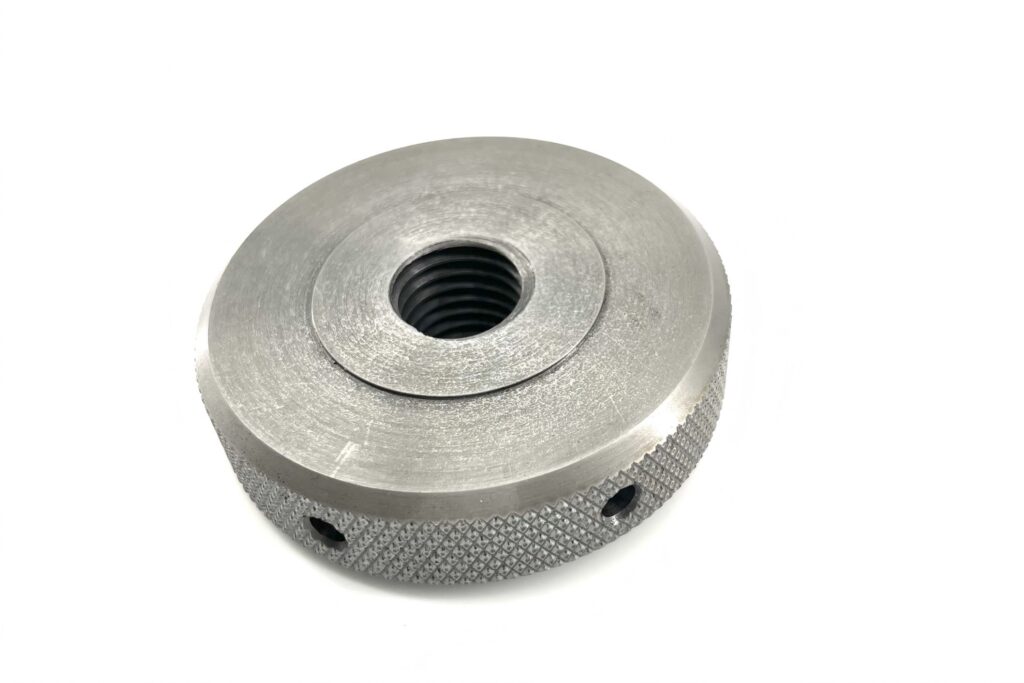
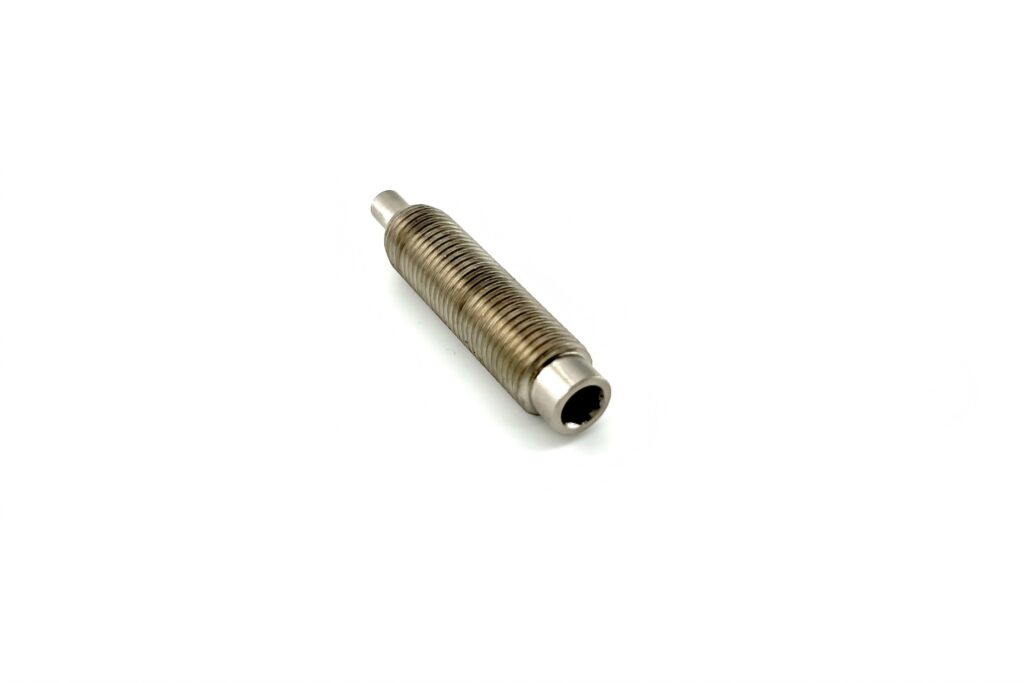
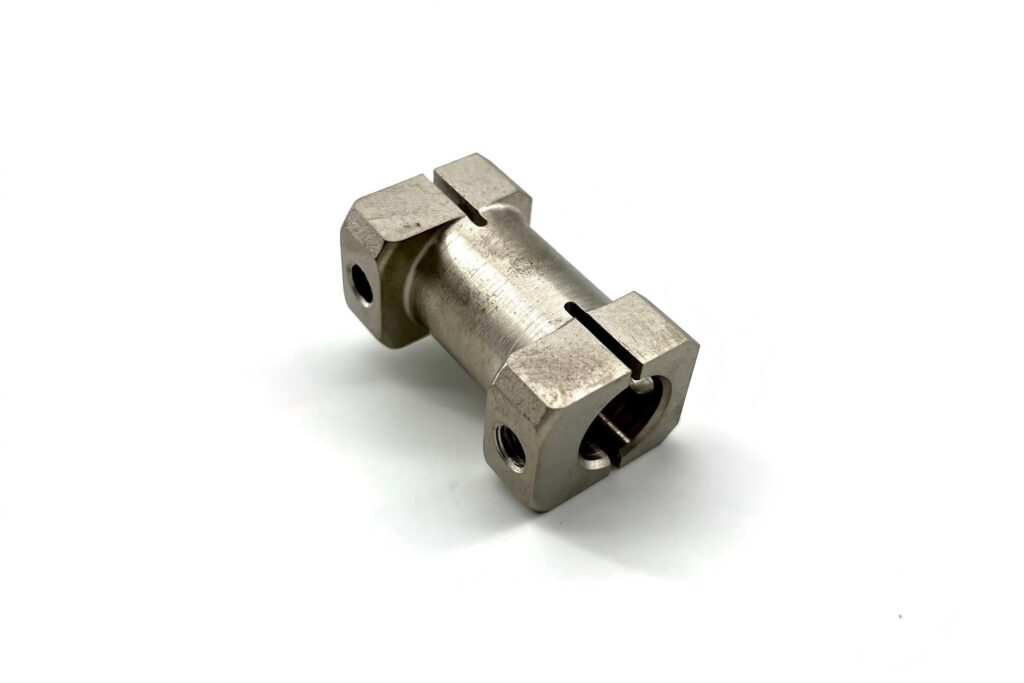
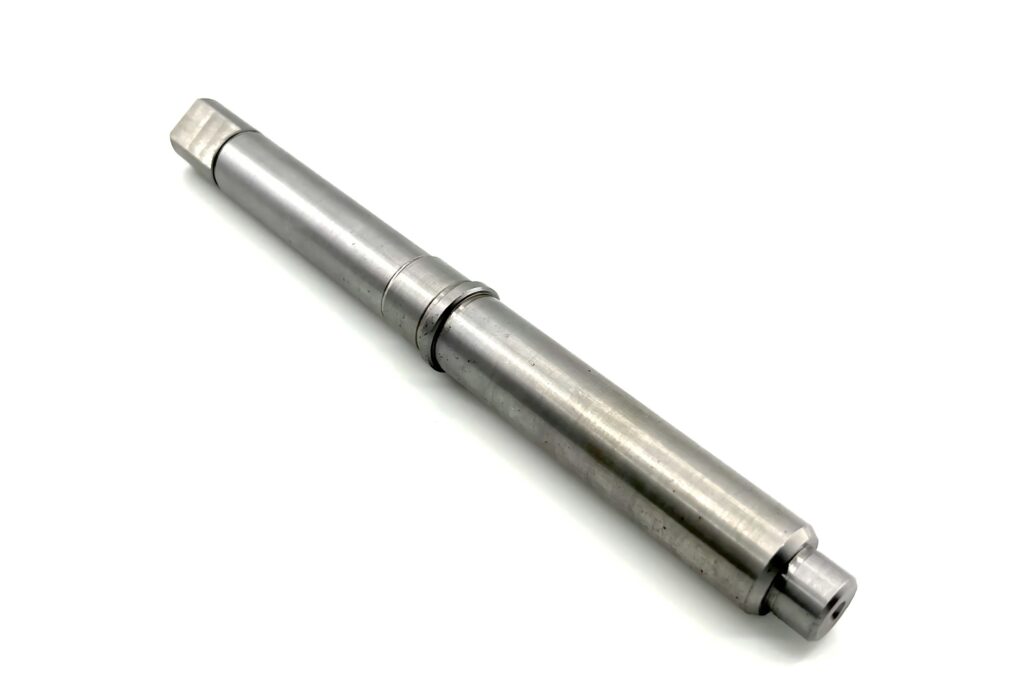




Sandblasting and Glass Beading
Sandblasting: A process that propels abrasive materials (e.g., silica sand, steel grit) at high speed to clean, roughen, or remove contaminants from a surface.
Glass Beading: A gentler process using fine glass beads for polishing or peening delicate surfaces.
Used in Aerospace, Automotive, and Medical.
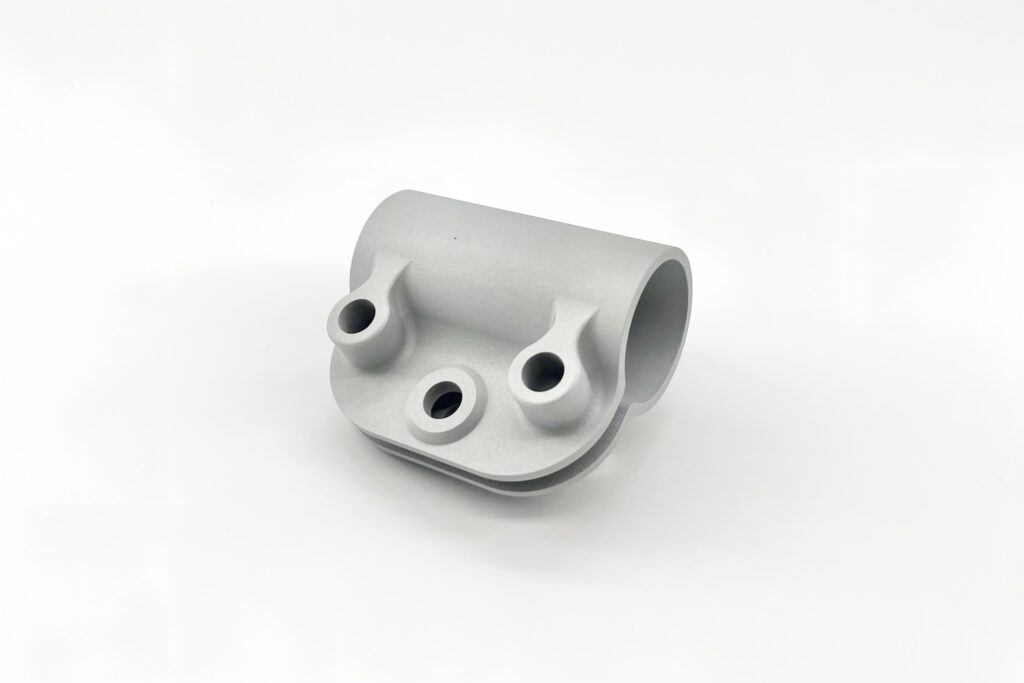
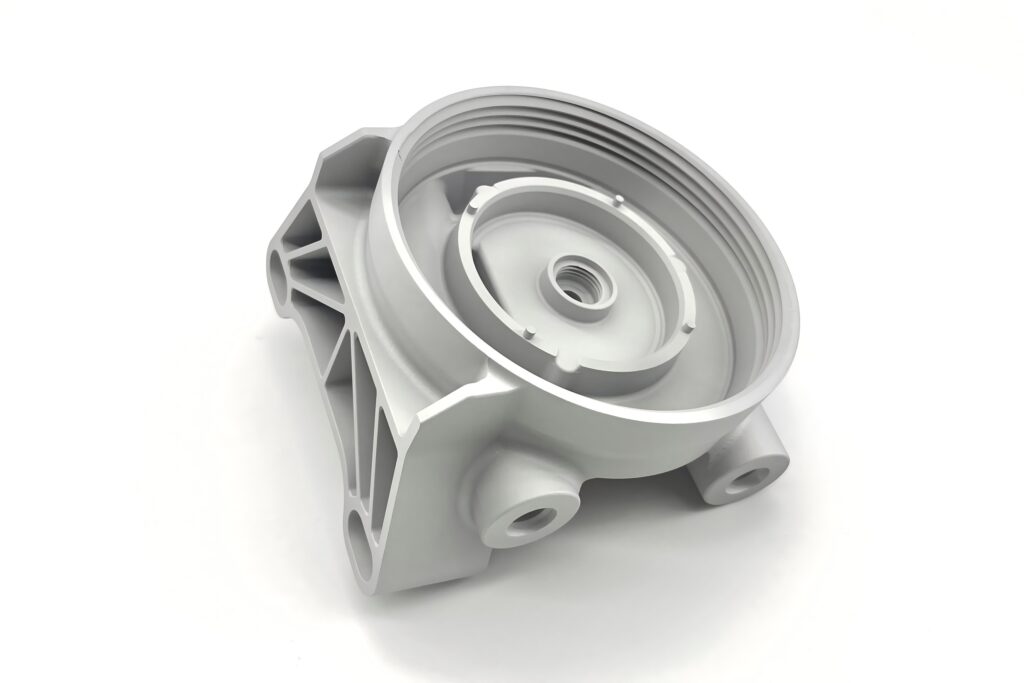
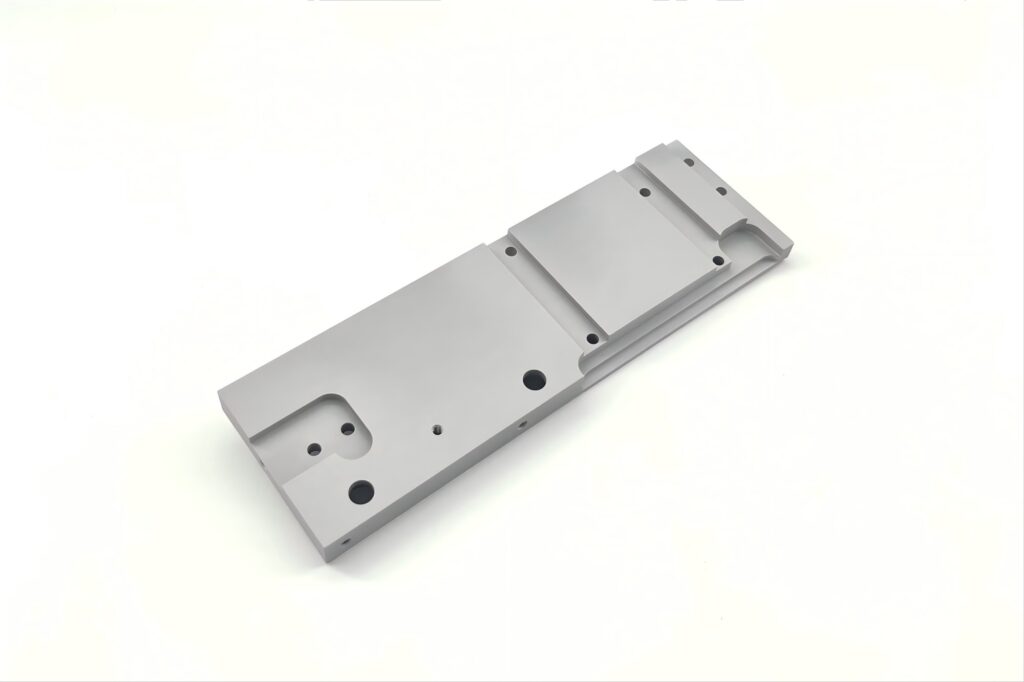
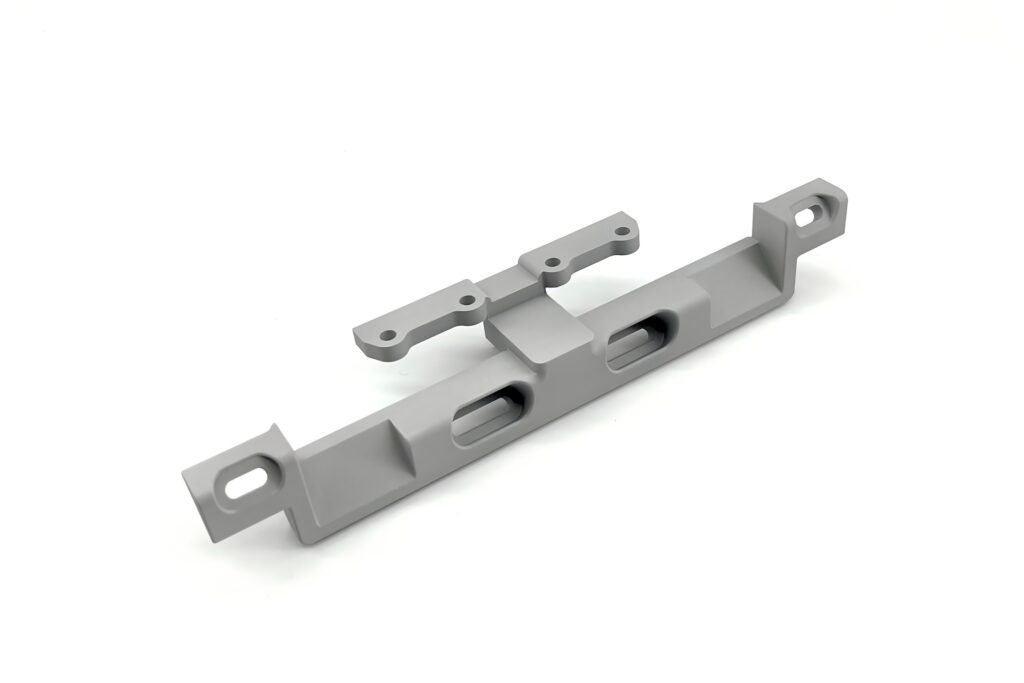




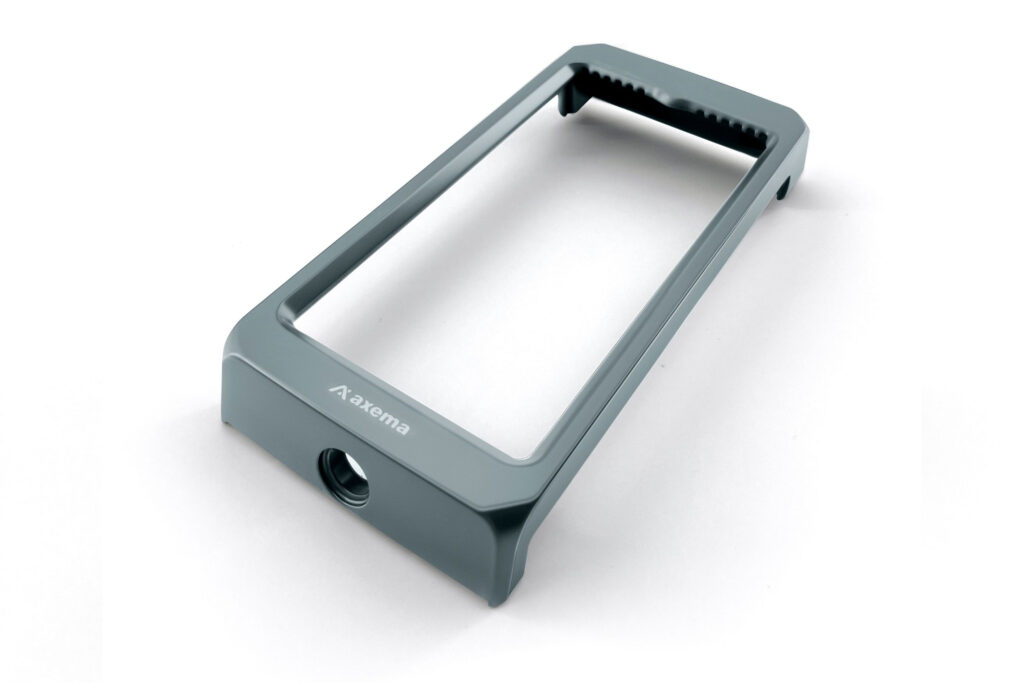
Polishing and Electroplating
Mechanical Polishin: A physical process using friction (with polishing wheels, compounds, or vibratory machines) to smooth and shine surfaces.
Electroplating: An electrochemical process that deposits a metal layer (e.g., chrome, nickel, zinc) to improve aesthetics, corrosion resistance, or conductivity.
Used in Aerospace, Automotive, and Medical.




Painting
Applies protective and decorative coatings via spraying or brushing, improving durability and color retention. Used in furniture, machinery, and consumer goods.